Experimental Solid Mechanics and Manufacturing Lab (ESMML)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Done Projects
Comparison of heel stresses in conventional and auxetic shoes: finite element modeling and experimental verification
Descriptions :
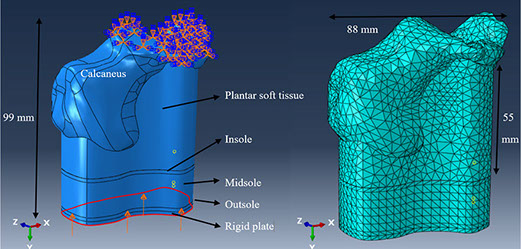
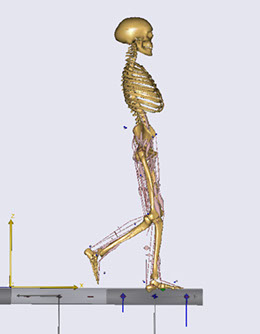
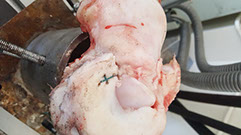
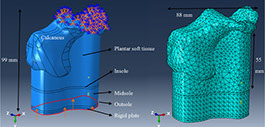
A three-dimensional finite element (FE) model of the heel and shoe sole was developed to analyze the effects of using materials with different Poisson's ratios for midsole on energy absorption and impact shock in the heel area during walking. The heel model was obtained from CT-scan data. The FE model was verified using Anybody software for barefoot with data obtained from gait analysis. Sole layers and plantar soft tissue were modeled, and five different Poisson's ratios (-0.4, -0.2, 0, 0.2, and 0.4) were compared for the midsole layer. In order to obtain the contact force, experiments were performed on a force plate using shoes with either auxetic or conventional midsole layer. Rayleigh damping theory was used to simulate viscous damping behavior in the midsole layer. The results showed that for materials with the same Young's modulus, there was less compression, energy absorption, and viscous dissipation energy in the auxetic model in comparison to the conventional model. However, when compressive strains of sole layers were the same (i.e., by changing Young's modulus), more energy absorption (about 9%) was observed for the midsole with negative Poisson's ratio with respect to the conventional midsole layer.
Keywords :
Auxetic; Finite Element Analysis (FEA); gait analysis; strain energy; shock absorption.
Supervisors :
Professor Amir Nourani
Students :
Mahdi Daei-Daei ,Mohammadmahdi Honarmand
Publications :
A. Nourani, M. Daeidaei, and M. Honarmand, “Finite element analysis of the performance of auxetic materials as shoe midsole, using force plate’s data”, Proceedings of 27th Annual International Conference of Iranian Society of Mechanical Engineering (ISME), Tehran (Iran), April 30 – May 2, 2019. coi
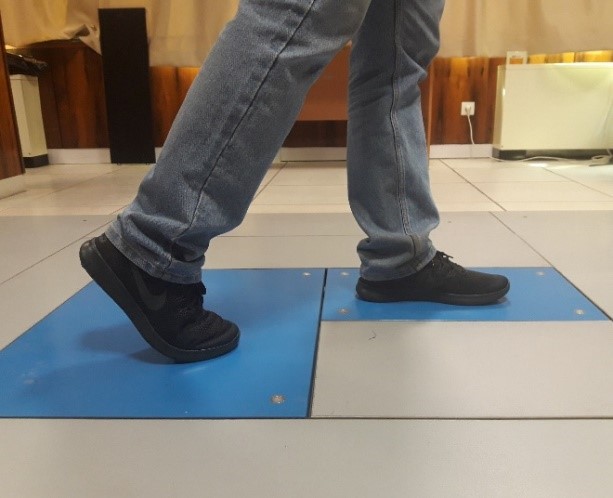

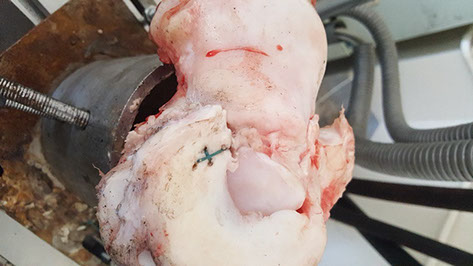
Walking on the force plate with Nike auxetic shoe
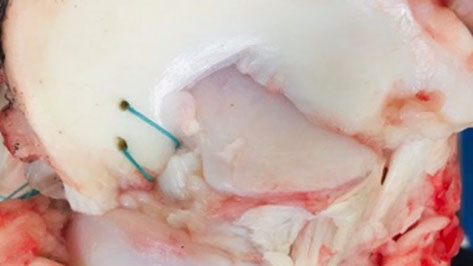
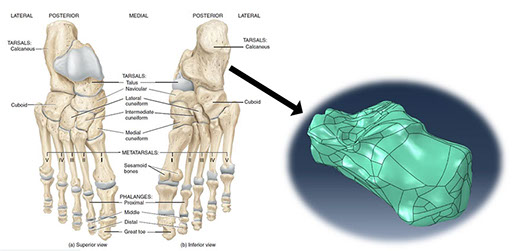
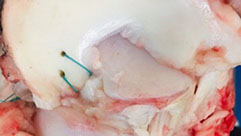
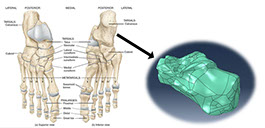
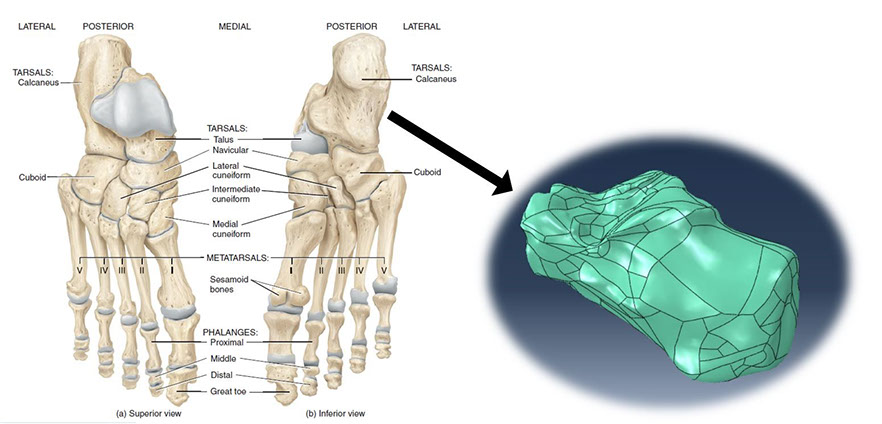
Skeleton of the foot consists of tarsal bones, including talus and calcaneus
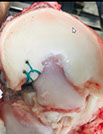
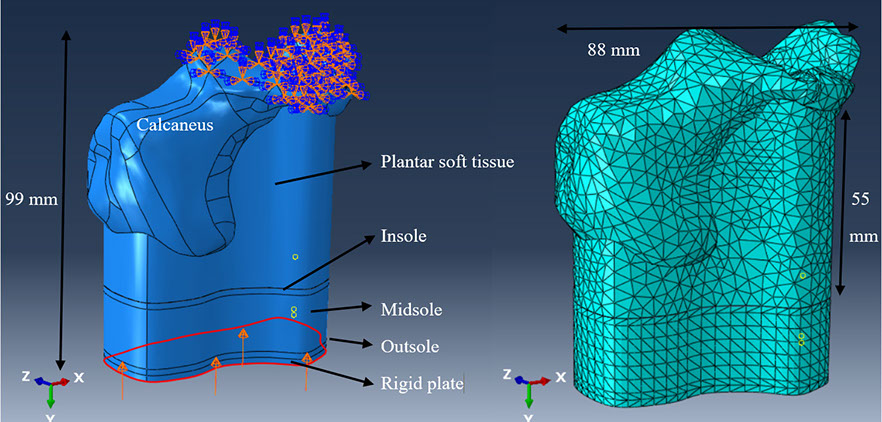
The boundary conditions and mesh used for the FE model.
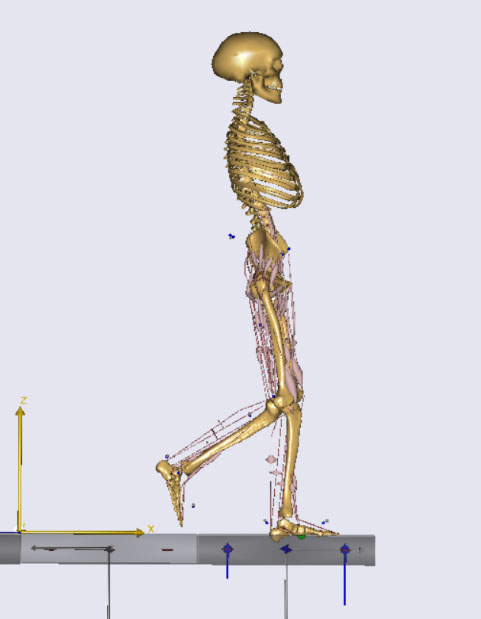
Gait model of the examiner walking on the force plate in Anybody software




Microelectronic Packaging
Descriptions :
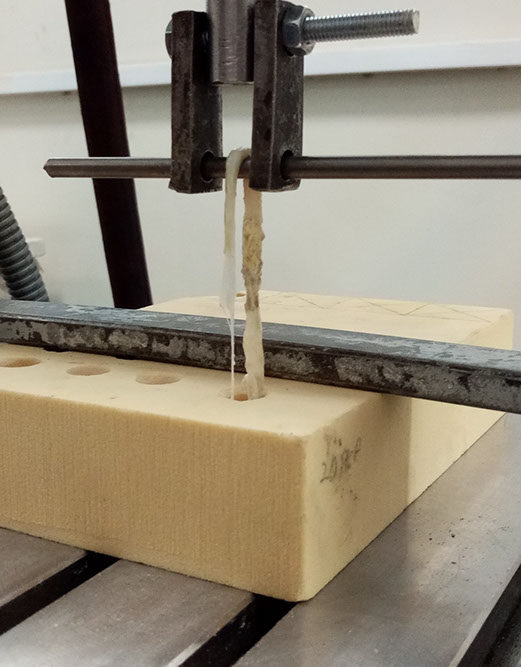
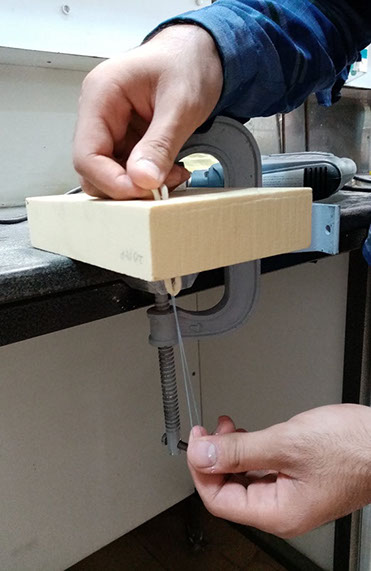
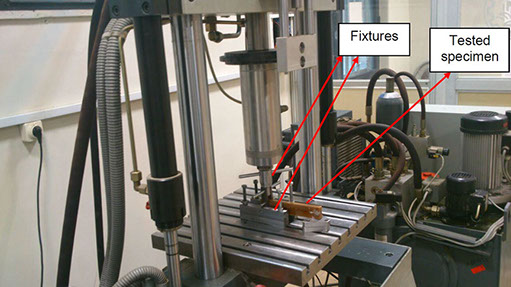
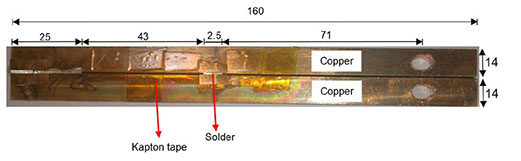
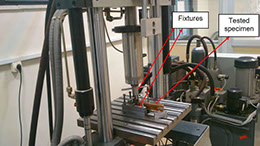
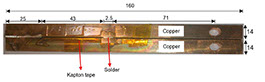
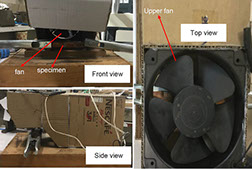
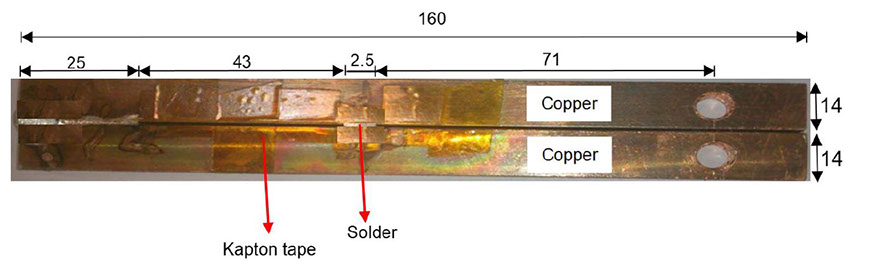
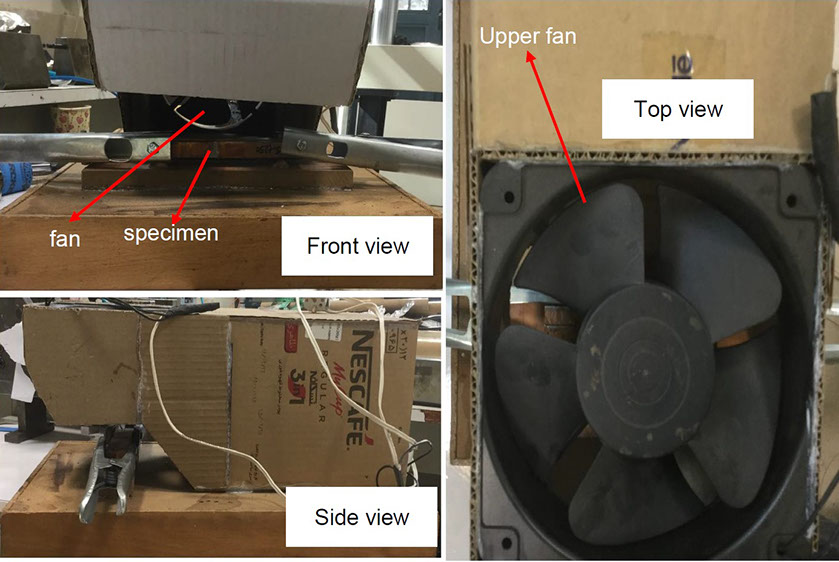
The ability to predict the fracture strength of solder joints would be a useful tool to assess the reliability of electronic devices. The vast majority of studies in the literature have dealt with the qualitative reliability testing of solder joints, while only a few studies have tried to give fundamental fracture property data that would be useful for fracture load prediction purposes. In this project, mode І critical strain energy release rate at crack initiation, Jci, of SAC305 solder joints between two copper substrates was measured using double cantilever beam (DCB) specimens at a strain rate of 0.03 s-1 as a function of bond-line width (i.e. joint size in the out-of-plane dimension), solder thickness, copper adherends thickness, suface roughness and joint arrangement.
Keywords :
Fracture behavior, solder joint, critical strain energy release rate, loading arm, load sharing, joint size/geometry.
Supervisors :
Professor. Ahmad Assempour
Assistant Professor. Amir Nourani
Students :
Sadegh mirmehdi, Mohammaamahdi Honarmand, Farid Soroush
Publications :
1- Influence of Joint Arrangement on the Fracture Behavior of Lead-Free Solder Joints.
2- Predicting Crack Initiation of Solder Joints with Varying Sizes Under Bending.
3- Predicting fracture of solder joints with different constraint factors.
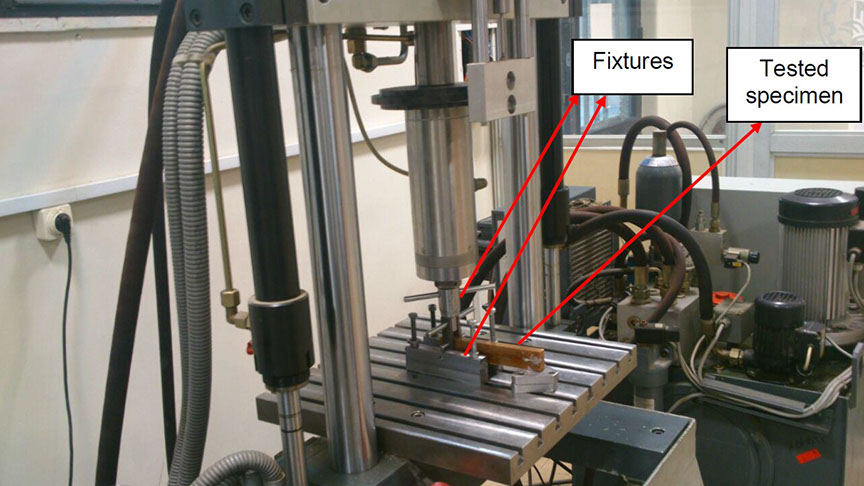

دستگاه هیدرولیکی مورد استفاده برای انجام آزمایشها
یک نمونه آماده شده برای آزمایش شکست. ابعاد به میلیمتر
تونل باد ساخته شده برای خنک کردن نمونه های لحیمکاری شده
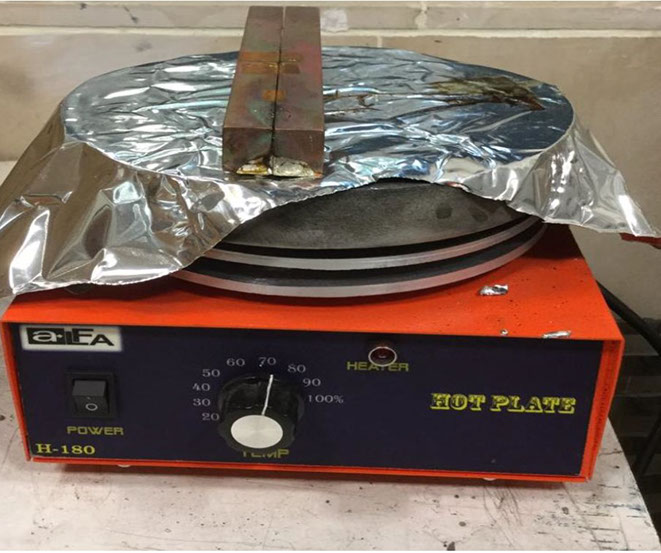
صفحه داغ مورد استفاده برای گرم کردن میله های مسی




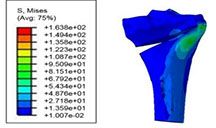
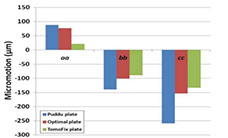
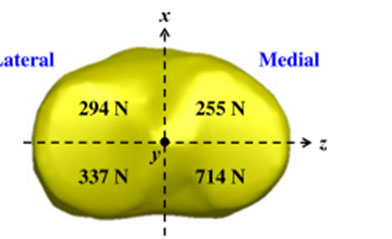
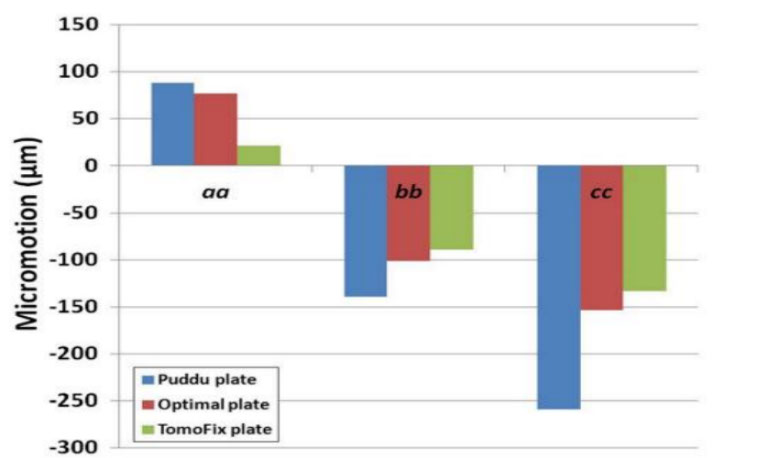
Evaluation of the structural role of implants in mechanoregulation of bone in high tibia osteotomy
Descriptions :
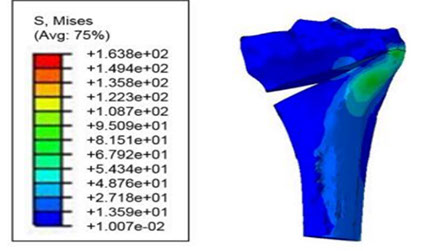
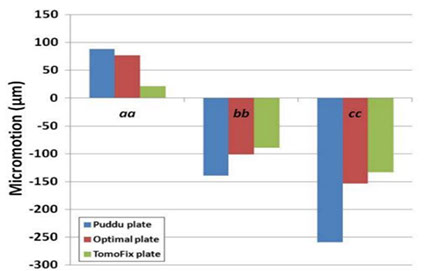
A medical image of the tibia has been modeled in Mimics to investigate the effects of implant's geometric parameters on mechanoregulation of bone in high tibia osteotomy. The stress analysis of bone and implants and the micro-motions under mechanical loads has been investigated in Abaqus software. The ultimate goal is to provide the proper environment for bone formation while maintaining system stability. Based on previous work, the Tomofix implant structure has been studied as the most suitable implant. Increasing the number of holes and shortening the tomofix implant are the modified parameters in this study. The results show that increasing the number of screws helps Tomofix improve bone formation and bring acceptable stability.
Keywords :
Implant, Mechanoregulation, Bone remodeling, FEM, Optimization, Biomechanics, Micro-motion, Stress shielding
Supervisors :
Dr. Amir Nourani
Students :
Ali Behbahani
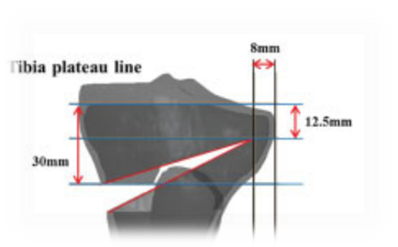






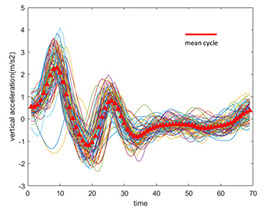
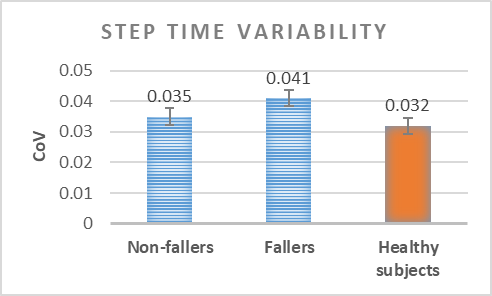
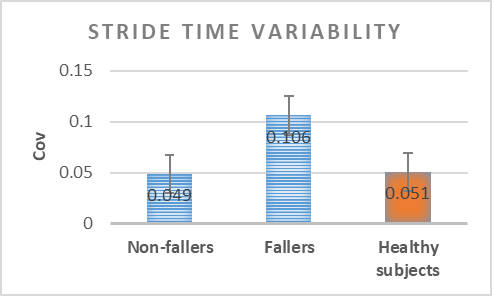
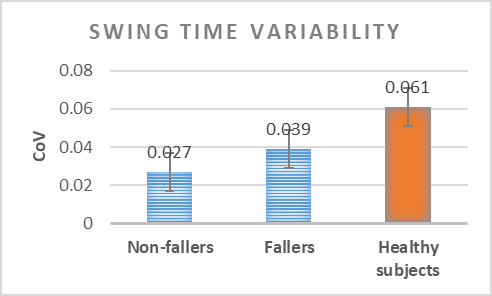
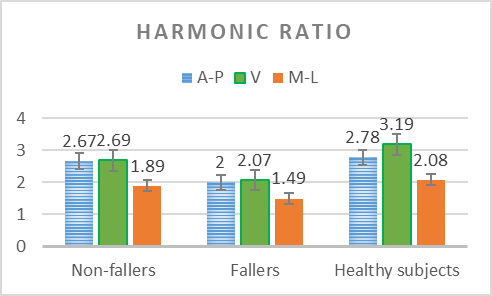
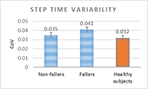
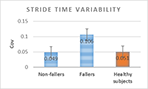
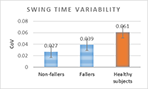
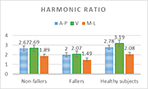
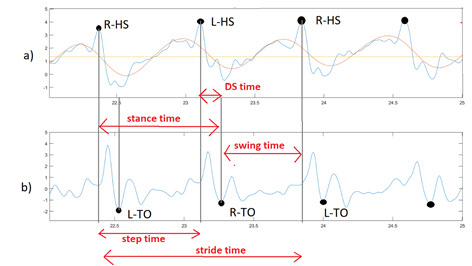
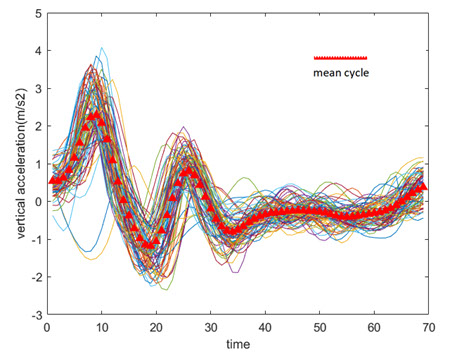
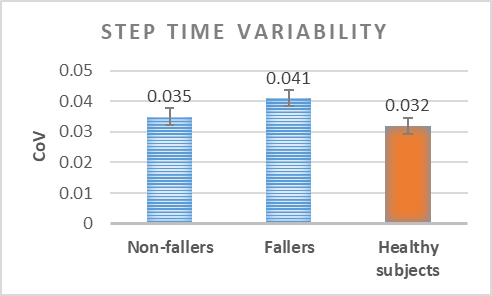
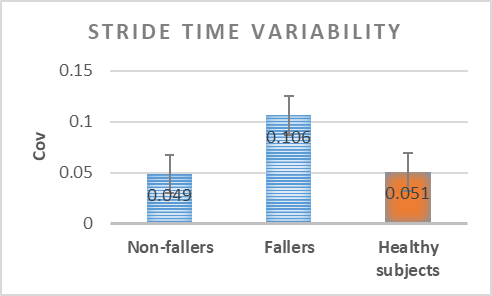
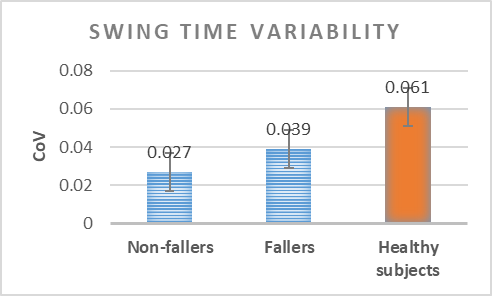
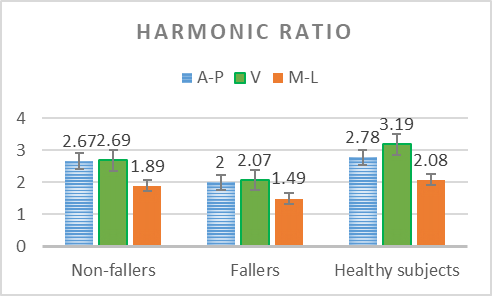
Analysis of the variability of gait cycle parameters based on upper body acceleration data obtained from Inertial sensors to predict the risk of falling
Descriptions :
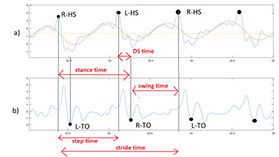
Variability in the values of gait cycle parameters is a measure of walking stability. Mental or physical disabilities usually manifest themselves in hand or foot movements. In this study, using the upper body acceleration data which was obtained from Inertial sensors, the variability of gait cycle parameters was investigated. Then, the reproducibility of the parameters in healthy individuals in this method was compared with the gold standard methods for healthy and sick elderly (at risk). The results showed that the step time parameter can be a suitable criterion as a standard method for separating healthy and sick people (at risk) as it had a good correlation with gold standard methods. Also, the variability of the step time parameter with a slight error compared to the gold standard methods can be considered as a suitable criterion; however, the variability of the swing time parameter showed a significant difference compared to the conventional methods. Investigating the variability of acceleration size in three anatomical directions showed that the acceleration in the anterior-posterior, and lateral directions had the highest repetition among healthy subjects.
Keywords :
Variability at the gait cycle, Inertial sensors, Upper body acceleration, Fall prediction, Variability at the upper body acceleration
Supervisors :
Dr. Amir Nourani
Prof. Farzam Farahmand
Students :
Ali Behbahani






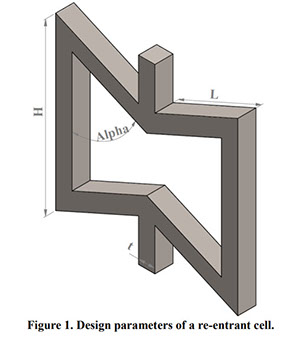
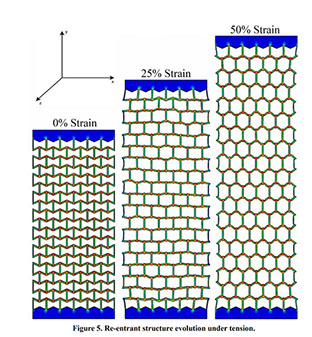
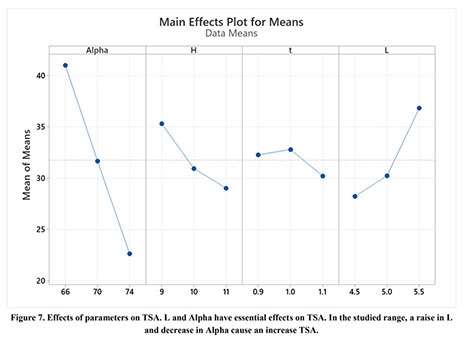
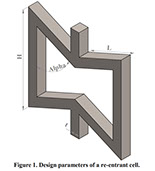
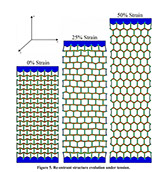
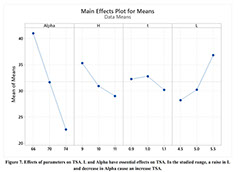
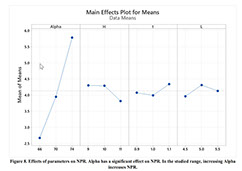
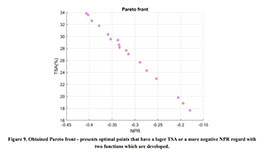
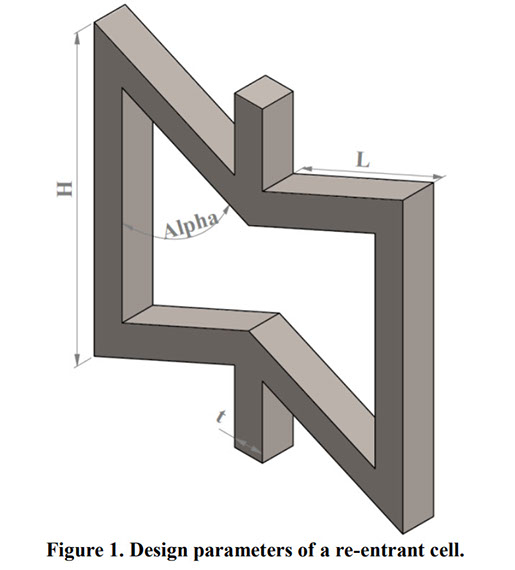
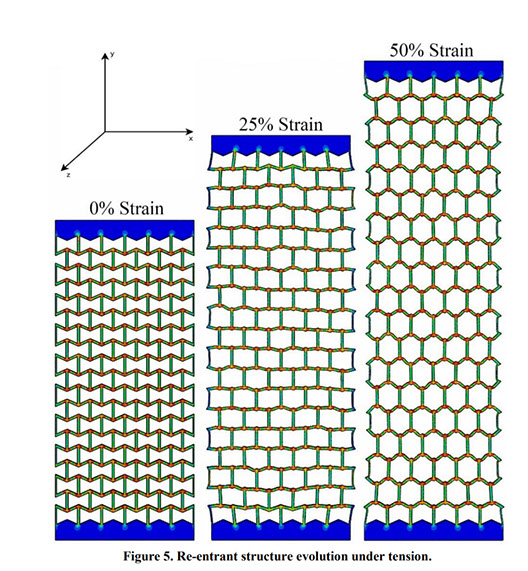
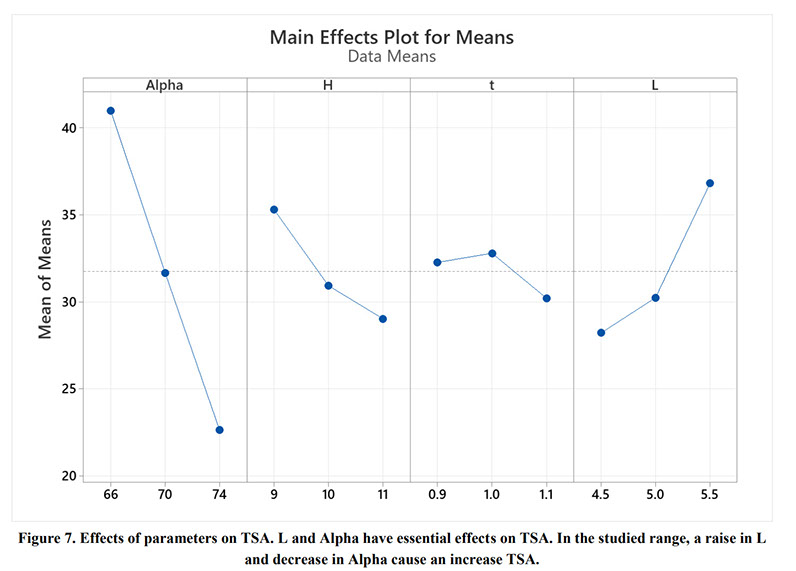
Parametric Analysis and Optimization of Auxeticity Range in Re-Entrant Hexagonal Structures
Descriptions :
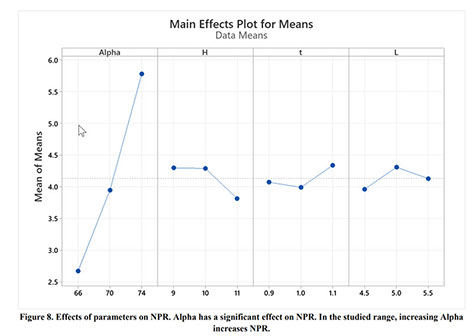
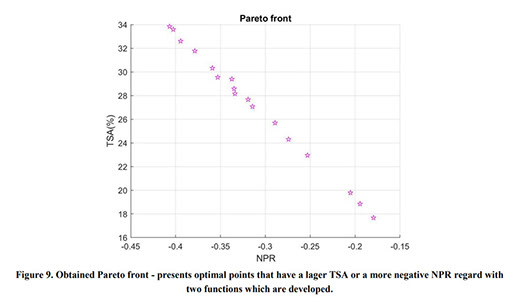
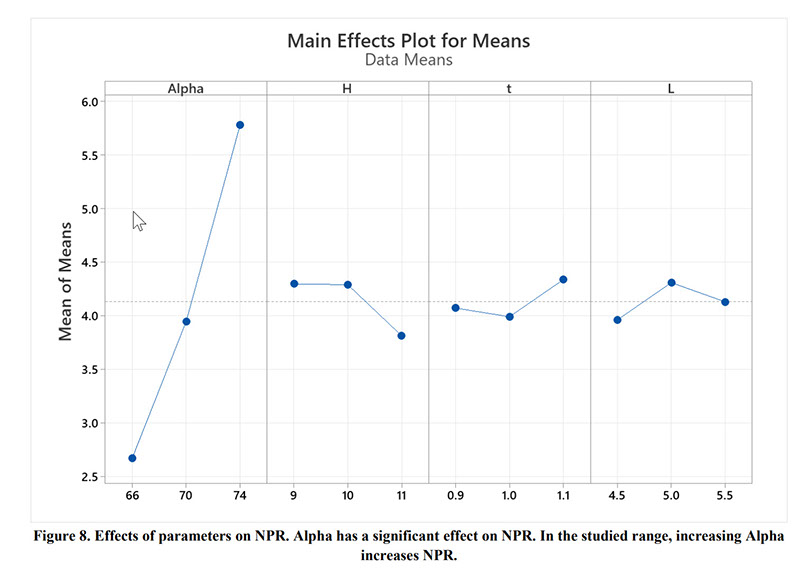
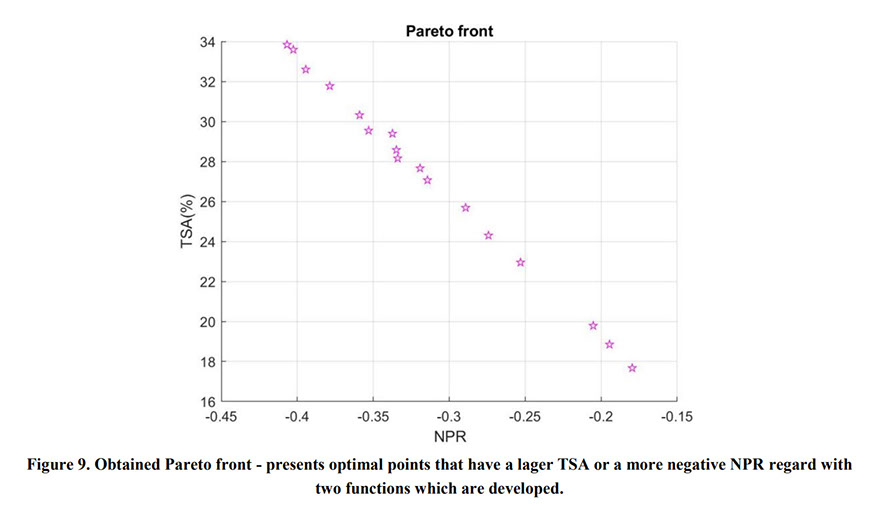
Auxetic metamaterials have a negative Poisson's ratio (NRP), and this irregularity makes them suitable for numerous engineering applications, such as enhancement in indentation resistance and energy absorption. The Poisson's ratio of re-entrant auxetic structures is highly strain dependent, and it can remain negative exclusively over a specific strain range. In re-entrant hexagonal cells, the Poisson's ratio increases with strain, surpasses zero, and becomes positive, which exterminates the auxetic characteristics of the structure. This study proposes a parametric analysis based on the structure geometry and performs a multi-objective optimization based on the auxeticity range and Poisson's ratio. A design of experiment (DOE) was carried out using the Taguchi method to find an empirical relation between Poisson's ratio and strain. The finite element method (FEM) was deployed to investigate the mechanical response of re-entrant structures to tensile loading. Using a statistical analysis, geometrical parameters were ranked based on their influence on Poisson's ratio. The empirical relation between the geometrical parameters, Poisson's ratio, and the auxeticity range was obtained to achieve the best geometrical configuration of the re-entrant structure using a genetic algorithm optimization. Finally, the best combination of geometrical parameters to increase the negative Poisson's ratio and extend the auxeticity region was represented.
Keywords :
Auxetic metamaterials, Negative Poisson’s ratio, Re-entrant hexagonal, Finite element analysis, Optimization
Supervisors :
Dr. Amir Nourani
Students :
Ali Behbahani, Sharif Sha'bani





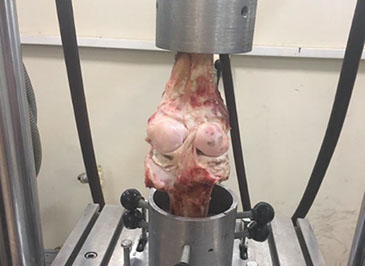
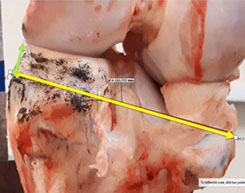
BASHTI (Bone And Site Hold Tendon Inside); A Brand New Implantless (Organic) Orthopaedic Fixation Technique
Descriptions :
In vivo test for analysis of the healing process, Analysis of drill size effect on fixation strength, Finite element modeling of Bashti technique, Developing Bashti technique for biceps injuries.
Keywords :
ACL Reconstruction; BASHTI Technique; Core Bone; Implant-less; Interference Screw; Tensile Test; Finite Element Method, Biceps Tenodesis
Supervisors :
Dr. Amir Nourani
Dr. Chizari
Students :
Amirhossein Borjali, Hadi Moeinnia, Mahdi Mohseni, Hossein Korani, Narges Ghias
Publications :
1- Comparison of mechanical properties in interference screw fixation technique and organic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction method: a biomechanical study, BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, October 2021 (Accepeted for Publication).
2- Core bone diameter in an organic implant-less technique affecting the biomechanical properties of the anterior cruciate ligament fixation; an in-vitro study
3- Effect of geometry on the fixation strength of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using BASHTI technique