

|
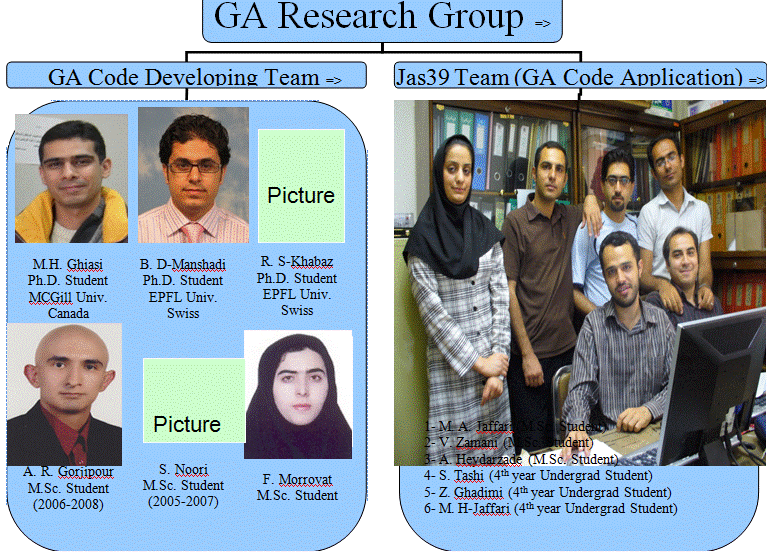
Research groups |






|
به نام خداوند جان و خرد سخنی از قرآن کریم |
|
GA Code Development - Summary Motivations:
∑ Manufacturing a full composite wing or the whole body of an aircraft requires an optimum tailoring of the composite laminate ∑ Since the searching space involved is a large,† non-convex, discrete, and fuzzy the GA approach suites the goal more than other optimization schemes ∑ GA needs to be adapted to the composite tailoring area
Objectives:
Developing the GA code and studying the main terms in GA for adapting to composites like:
†††† ††† ††††† Penalty functions†††††††† †††††††††††† †††††††††††† Population size†††††††††††† †††††††††††† ††††††††††† †††† ††† ††††† Initial population††††††††† †††††††††††† †††††††††††† GA operators †††† ††† ††††† Fitness Scaling†††††††††††† †††††††††††† †††††††††††† Stopping criteria
Results:
∑ A two part penalty (combination of Death-Dynamic penalties) was developed ∑ The best values of GA operators like mutation, cross over, elitism, etc. were defined and applied to the GA code. ∑ A new logarithmic stopping criteria was developed and applied ∑ A smart way of defining the initial population was invented ∑ The effect of population size was also studied.
Publications:
1) Abedian, A., Ghiasi, M.H., Dehghan-Manshadi, B., "An introduction to a new criterion proposed for stopping GA optimization process of a laminated composite plate", Journal of Aerospace Science and Technology (JAST), Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 167-176, 2006. 2) Abedian, A., Ghiasi, M.H., Dehghan-Manshadi, B., "Effects of a linear-exponential penalty function on the GA's Efficiency in Optimization of laminated composite panel", International Journal of Computational Intelligence (IJCI), Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 5-11, 2005. 3) Salehi, S. M., Abedian, A., "Effects of genetic Operators on the Optimum Tailoring of Laminated Composites Using GA", Proceeding of the 7th International Conference of the Iranian Aerospace Society, Tehran, Iran, 2008.
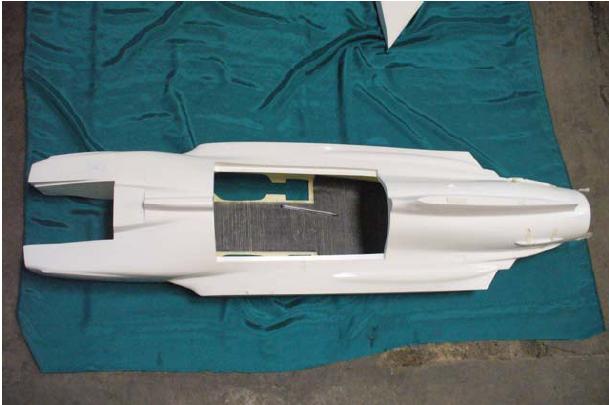
Jas39 Model Motivations: ∑ As a test case for the GA code the model of Jas39 aircraft was chosen to be simulated and then manufactured
Objectives: ∑ Each major part of the aircraft is studied by one student: †††† ††† †††††Nose (Amir)†††† †††††††††††† †††††††††††† †††††††††††† †††† ††††††† †††††Wing (Vahid)††††††††† ††††††††††† †††† ††† ††††† Fuselage (Mohamed)†† †††††††††††† †††††††††††† †††† ††††††† †††††Tail (Samaane) †††† ††† †††††Canard (Zahra)†††††††††††† †††††††††††† †††††††††††† †††††††††††† ††††† Loading-Xplane (Mohamed)
Jas39
|